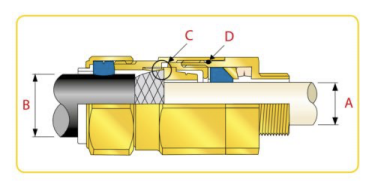
Cable glands
Cable glands are defined as ‘mechanical cable entry devices’ which are used in conjunction with cable and wiring for electrical, instrumentation & control, and automation systems, including lighting, power, data and telecoms.
The main functions of the Cable Gland are to act as a sealing and terminating device to ensure the protection of electrical equipment and enclosures, including the provision of: